Quartz
Material
Single-crystal quartz (SiO2) is a crystal that occurs both naturally and is produced synthetically using hydrothermal synthesis. In the wavelength range between 0.3 µm and 2.7 µm, the transmission percentage is over 90 %. In contrast to quartz glass, monocrystalline quartz has a strong birefringence. Quartz is normally present as alpha quartz (low quartz), at a temperature above 573 °C the crystal structure changes to beta quartz (high quartz). This is a reversible process, but it can lead to cracks and fractures in the material.
Quartz is mainly used as a polarizer, in piezoelectric components, in FIR optics, as a VUV filter and in microscopes.
Properties
Spectral properties
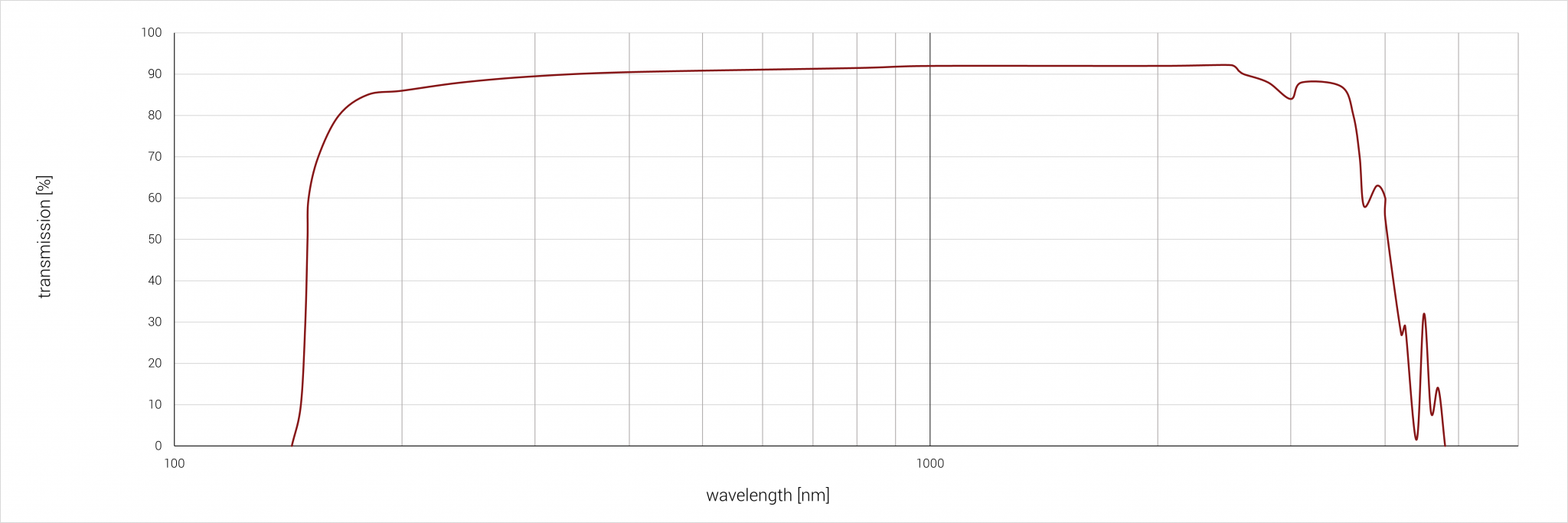
Sample thickness: 2 mm

